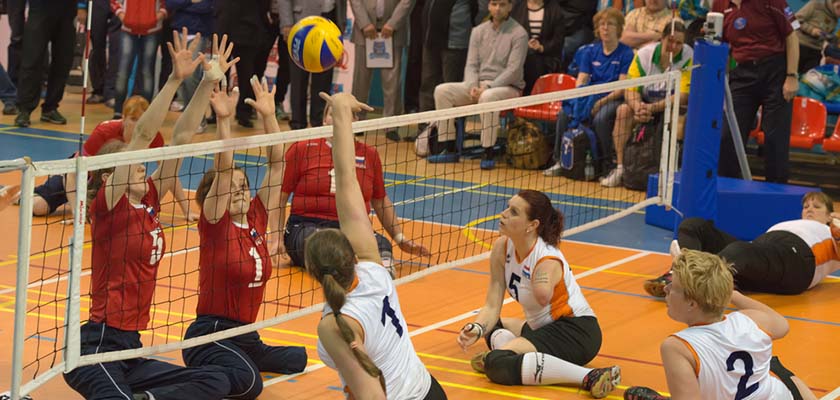Did you know you can play sitting volleyball? This method was developed to promote the inclusion of disabled athletes and is now part of the Paralympic Games. Find out all about sitting volleyball and what the sport represents.
Sitting volleyball – also known as paralympic volleyball – is an adaptation of conventional volleyball for those with walking difficulties. Here’s a look at how it works, its purpose and fundamentals.
Participate in our free Whatsapp community and receive daily tips, news and trivia from over 50 sports! Click here to participate.
How does sitting volleyball work?
Sitting volleyball works in much the same way as traditional volleyball, but players compete while sitting on the floor, which allows athletes with different types of physical disabilities to take part.
The sport involves teams of six players on each side of the court. The matches are played in best of five sets, with some adaptations to the rules compared to conventional volleyball to accommodate the limitations of seated players.
The sport has grown in popularity since its inclusion in the Paralympic Games and is a significant way of establishing equality.
The aim of sitting volleyball
The objective of sitting volleyball is the same as conventional volleyball: to score points by keeping the ball in play and making it touch the ground on the opponent’s side of the court, while preventing the ball from touching the ground itself.
It’s a sport that helps develop skills such as teamwork, coordination, strategy and overcoming challenges.

Sitting volleyball fundamentals
The fundamentals of sitting volleyball are very similar to those of the traditional sport: passing (reception), setting, attacking, blocking, defending and serving. Below, you can see each of them in more detail:
Pass (reception)
Players must receive the ball properly, using their hands, forearms or other parts of their body to control the trajectory of the ball and direct it towards their teammates.
Survey
After the pass, a player must execute the pick-up, which is the gesture of touching the ball with the hands in a controlled manner to direct it towards an attacker.
Attack
One player (or several) carries out the attack, trying to send the ball to the opponent’s side of the court in order to score points.
Block
Players can make blocks, trying to intercept opponents’ attacks and prevent the ball from going over the net.
Defense
The players must defend their opponents’ attacks, trying to prevent the ball from hitting the ground on their side of the court.
Sack
In the serve, a player hits the ball in such a way as to throw it to the opponent’s side of the court.
All about sitting volleyball: how it came about
But then how sitting volleyball came about: it was in Holland in the 1950s. Originally, the idea was to involve soldiers wounded during the Second World War.
Sitting volleyball was invented by a group of doctors and therapists who were looking for ways to reintegrate these wounded soldiers into society and help them with physical activities.
So in the beginning, sitting volleyball was a form of occupational therapy, but it soon evolved into a competitive sport.
All about sitting volleyball: disciplines
The modalities of sitting volleyball are the classic ones:
- Men’s sitting volleyball
- Women’s sitting volleyball
The two main disciplines of sitting volleyball are played both at the Paralympic Games and in smaller competitions around the world. In both cases, the teams consist of six players.
All about sitting volleyball: who can play?
As the Brazilian Paralympic Committee points out, who can play sitting volleyball is basically anyone (man or woman) who has a physical or locomotion-related disability, i.e. one that affects mobility, such as:
- Paraplegia: partial or total paralysis of the legs, resulting in difficulty or inability to move the legs.
- Tetraplegia: partial or total paralysis of the upper and lower limbs, affecting the arms and legs.
- Amputations: total or partial loss of limbs, such as legs, feet, arms or hands, which can affect athletes’ mobility.
- Poliomyelitis: sequelae of poliomyelitis that result in muscle weakness, deformities or partial paralysis.
- Spinal cord injuries: injuries to the spinal cord that cause partial or total paralysis of the lower limbs.
- Congenital malformations: congenital conditions that affect the development or structure of the limbs, resulting in walking difficulties.
All about sitting volleyball: classes
The classes of sitting volleyball are divided according to the degree of disability. Basically, athletes are divided into two groups: VS1 and VS2.
- VS1: athletes with more severe disabilities that have a greater impact on the essential functions of sitting volleyball, such as leg amputees.
- VS2: athletes with milder disabilities and less interference with their functions on the court, such as amputation of part of the foot
All about sitting volleyball: Brazilian national team
The Brazilian sitting volleyball team made its Paralympic Games debut in Beijing 2008 with just the men’s team, which finished sixth in the competition.
At London 2012, Brazil had representatives in both genders, with both the men’s and women’s national teams coming fifth.

What titles has the Brazilian national sitting volleyball team won?
The Brazilian national sitting volleyball team won its first title at Rio 2016, with bronze for the women’s team. Another bronze came in Tokyo 2020. In 2022, the Brazilian women’s sitting volleyball team won the world championship in Sarajevo, Bosnia.
Now that you know all about sitting volleyball, how about keeping up to date with the world of sports? Be sure to follow our content: